Market leaders like Microsoft, Amazon and J.P. Morgan already have live blockchain operations in place. The infrastructure is starting to be used for everything from payment verification and wealth management to asset trading and identity protection.
That growth looks to continue, with annual global spending on blockchain solutions estimated at $11B today, and that number is expected to roughly double within 24 months.
But what exactly is blockchain, how does it work and what are the implications for the association industry?
What Is Blockchain?
At its core, blockchain is a glorified database.
However, this database is shared across multiple computers on a network. The records within it are called "blocks" and these blocks are chained together in series. This happens through a unique, electronic code that links each block to the previous blocks.
All the data is publicly viewable to everyone on the network. Moreover, all activity is verified through a form of cryptography. Thus, blockchain forms a decentralized record of transactions that is both transparent and secure.
It does this by replicating the data across all nodes of the network, with every participant holding an identical copy of the information. Such duplication provides an immutable, transparent and append-only register of all the actions that have happened. All of that information is then fully secured using cryptographic features, such as a hash function, a digital signature and encryption.
The Impact
Transactions that are verifiable through coding suddenly create the potential for an entirely new business model.
Remember, those records cannot be easily altered because of the chaining of the data. Also, the network is resistant to hacking because that data is distributed. This leads to a new financial reality: fiduciary institutions like a bank or even a government suddenly become unnecessary.
There is no longer any need for third-party oversight to create trust between the parties to a transaction. Thus, blockchain removes all middleman institutions from any financial engagement. Banks, brokers and technology firms disappear from the transaction process. Obviously, this would significantly reduce cost, time and risk regarding security.
The real advancement isn't so much how the technology works. It's really the fact that blockchain now creates ‘digital trust.’ In turn, this has the ability to revolutionize the way we exchange value over the internet.
How Blockchain Works
But how exactly does blockchain work?
When any transaction occurs, every computer on the network attempts to verify the transaction. It's important to note that the decision to add a transaction to the chain is made by group consensus. This means that the majority of computers in the network agree that the transaction is valid, which is often done by one of two methods.
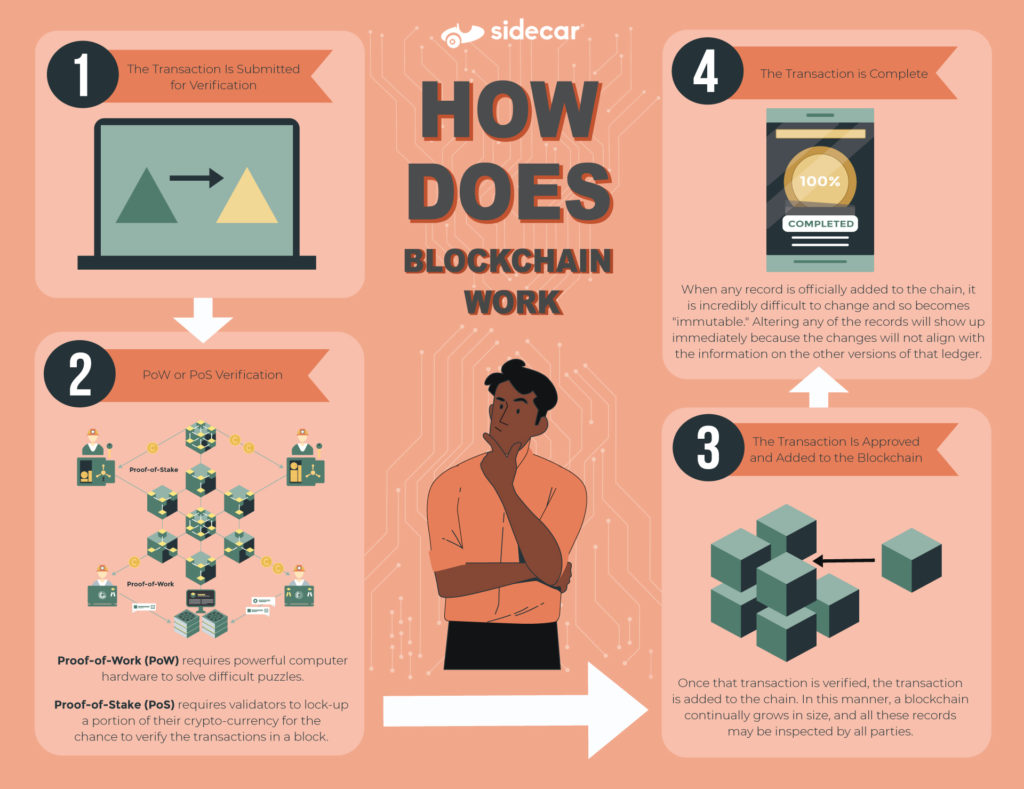
- Proof-of-Work (PoW): The people who own the computers in the network are incentivized to verify these transactions through rewards. This process is known as ‘proof of work’ and solving the math problem is known as "mining." The folks who do the verifications are rewarded for their work with cryptocurrency compensation.
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS): As a way to reduce the amount of computing power needed to validate a transaction, the PoS method was created. This method requires validators to lock up a portion of their crypto-currency for the chance to verify the transactions in a block. The validators are chosen at random based on the amount of crypto they stake, and once a specific number of these validators verify a transaction, it is added to the blockchain.
Once that transaction is verified, it is added to the chain. In this manner, a blockchain continually grows in size, and all these records may be inspected by all parties. The growth of the database effectively adds security to the ledger, over time.
When any record is officially added to the chain, it is incredibly difficult to change and so becomes "immutable." Altering any of the records will show up immediately because the changes will not align with the information on the other versions of that ledger. This data alignment is the benefit provided by multiple copies of the database.
9 Benefits of Blockchain Technology
This "distributed ledger" technology brings several key benefits.
Primarily, blockchain is:
- Trustworthy - Two parties who neither know nor trust each other can safely conduct business together because the coding creates the trust.
- Decentralized - there is no longer any need for a central authority to be involved in every transaction.
- Secure - all records are individually encrypted.
- Cost-Effective - eliminates middlemen, vendors and third-party providers
- Anonymous - identities of participants in transactions are anonymous.
- Traceable - every transaction is visible, time-stamped and traceable.
- Unanimous - all network participants agree on the validity of each record.
- Immutable - all validated transactions are irreversible and cannot be changed or deleted. This means data accuracy.
- Distributed - all network participants have a copy of the ledger for total transparency.
What Association Pros Need to Know
It’s important to note that blockchain is broader than just finance. It also holds the possibility of better managing complex processes like the storing of medical records, administering of government benefits and even voting.
It can be applied to any multi-step transaction where traceability and visibility are required. The growth of blockchain is due to the fact that firms, customers and suppliers can now collaborate in a secure, auditable and virtual way.
For the association space, that means blockchain can have on a range of industries, including:
- Real Estate: In real estate, blockchain can replace the paper records used in transferring deeds of homes and land. Rather than issuing a paper title, property titles can be stored on the blockchain, creating an easily accessible, clear documentation of ownership. It can even codify fractional ownership of real estate.
- Events: Industry events are a big part of the association industry. Blockchain is directly applicable to conferences and gatherings. This is because blockchain technology facilitates everything from venue sourcing and ticketing to the managing of sponsors and attendees.
- Credentialing: In the education space, blockchain could help manage the process of record-keeping and credentialing. It would be directly applicable to storing digital curriculums and the unlocking of progressive lessons by smart contract for each individual student.
On the whole, blockchains improve recordkeeping processes, speed asset transfers, provide secure identity protection and enable faster reconciliation. Yet of the many benefits, the key takeaway is really the trust that blockchain creates.
In the world ahead, there may well be a single source of truth that stores events, ownership and activities involving multiple parties - all without the use of separate systems and with no reconciliation required. Such a revolution would change the way digital services are provided across all industries globally.
Exactly how this will play out, is not yet clear. What is clear is that both disruption and opportunity are coming – get ready.
Tags:
Association Management
February 15, 2022